Industry 4.0: More Than Just Speed – It’s About Sustainability
Modern manufacturing is undergoing a high-tech transformation. But it’s not just about faster production—it’s about greener, more efficient operations.
You’ve probably heard terms like Industry 4.0, IoT, and smart factories. What do they mean?
- Using real-time data and automation to make factories smarter and more efficient.
- That efficiency directly leads to lower energy use and reduced emissions, helping manufacturers achieve:
- SDG 7 (Clean and Affordable Energy)
- SDG 13 (Climate Action)
How Smart Factories Save Energy
1. Predictive Maintenance: Stopping Energy Waste Before It Starts
Imagine every machine in your factory has smart sensors feeding data into a central system.
- If a motor starts consuming more power than usual, the system alerts maintenance before excess energy is wasted (or before the machine breaks).
- This prevents downtime, reduces costs, and optimizes energy use.
✅ Example: A factory using predictive maintenance cut unnecessary energy use by 15% just by fixing underperforming equipment early.
2. Smart Climate Control: Cooling and Heating Only When Needed
- Smart systems adjust heating and cooling based on:
- Weather conditions
- Room occupancy
- Production schedules
- No more cooling an empty warehouse—every adjustment means less wasted energy.
3. AI-Powered Production Scheduling
AI can fine-tune production schedules to minimize energy waste:
- Running energy-heavy processes when solar panels are producing peak power
- Aligning production with low electricity rate periods (which often means the grid is using more renewable energy)
✅ Example: One automotive factory reduced its electricity use by 10% just by optimizing its schedule.
4. Robots and Precision Manufacturing: Cutting Waste, Cutting Energy
- Automation and robotics improve precision, reducing errors and material waste.
- Less rework = less energy used on fixing mistakes.
5. Digital Twins: Simulating Efficiency Without Risk
A digital twin is a virtual model of your production line.
- Companies use digital twins to test process changes before applying them in real life.
- This allows factories to experiment with efficiency improvements without causing downtime or disruptions.
✅ Example: A manufacturer modeled waste heat recovery in a digital twin before installing equipment—resulting in 30% more energy savings than expected.
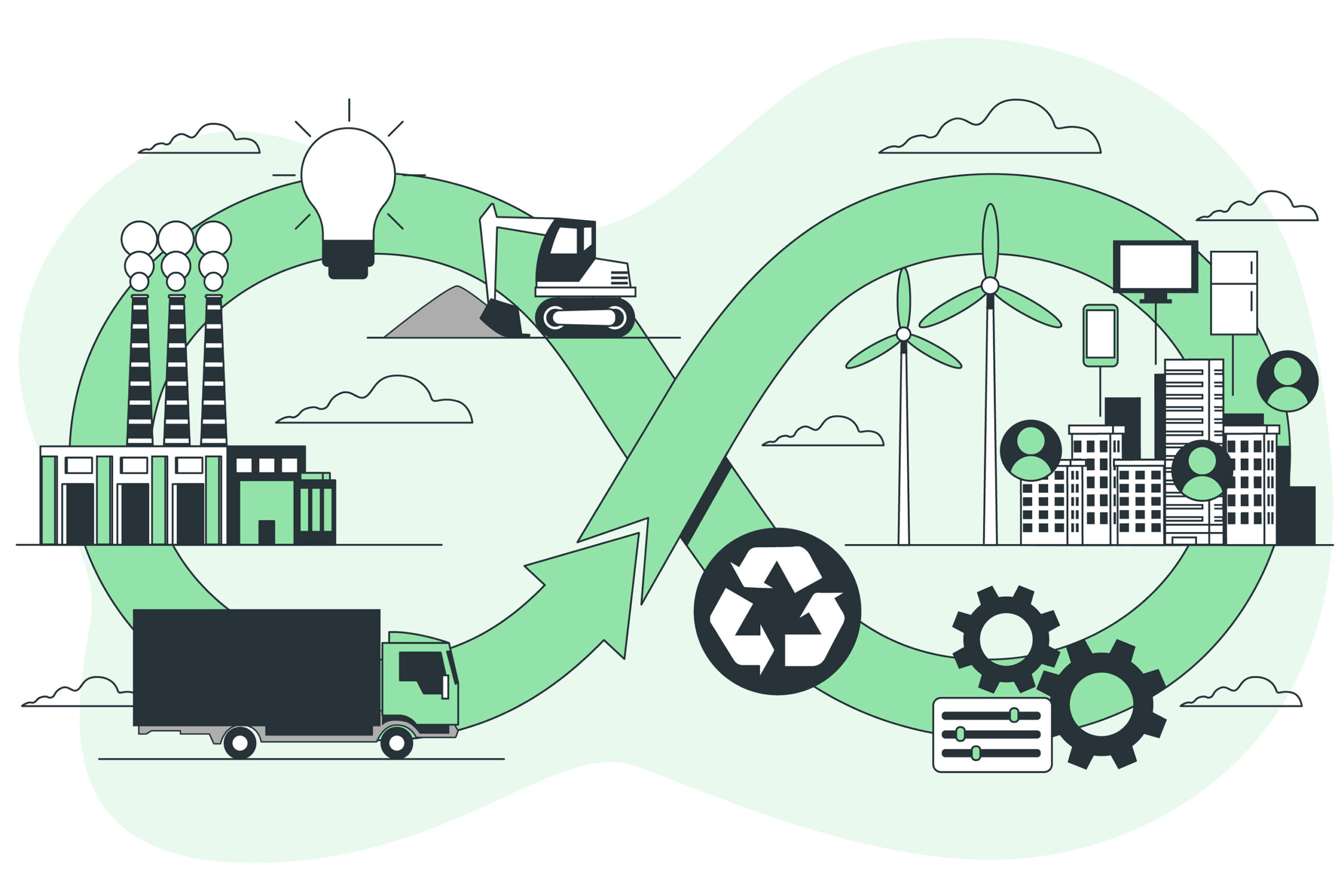
The Smart Factory Cycle: A Continuous Loop of Efficiency
Smart factories create a cycle of improvement:
- Gather real-time data
- Analyze inefficiencies
- Implement solutions
- Monitor impact and repeat
The result? A leaner operation with lower energy use and a smaller carbon footprint.
Why Smart Factories Are a Win for Business and the Planet
✅ Lower Energy Costs – Smarter operations mean lower power bills.
✅ Reduced Emissions – Less energy wasted means lower carbon footprints.
✅ Better Productivity – Automation and AI boost output while cutting waste.
✅ Stronger Brand Image – A high-tech, green factory is a competitive advantage.
Conclusion: Industry 4.0 as a Path to SDG 7 & SDG 13
By embracing IoT, AI, automation, and digital twins, manufacturers can reduce waste, cut energy use, and lower emissions—all while improving productivity.
Smart factories are not just the future—they are the key to sustainable, competitive manufacturing today.









Leave a Reply